Cybersecurity After the Sale: Who’s Watching Your Back?

Change is a defining feature of the cybersecurity landscape. It brings progress, enabling smarter tools and stronger defences to meet ever-evolving threats. But not every shift moves things in the right direction.
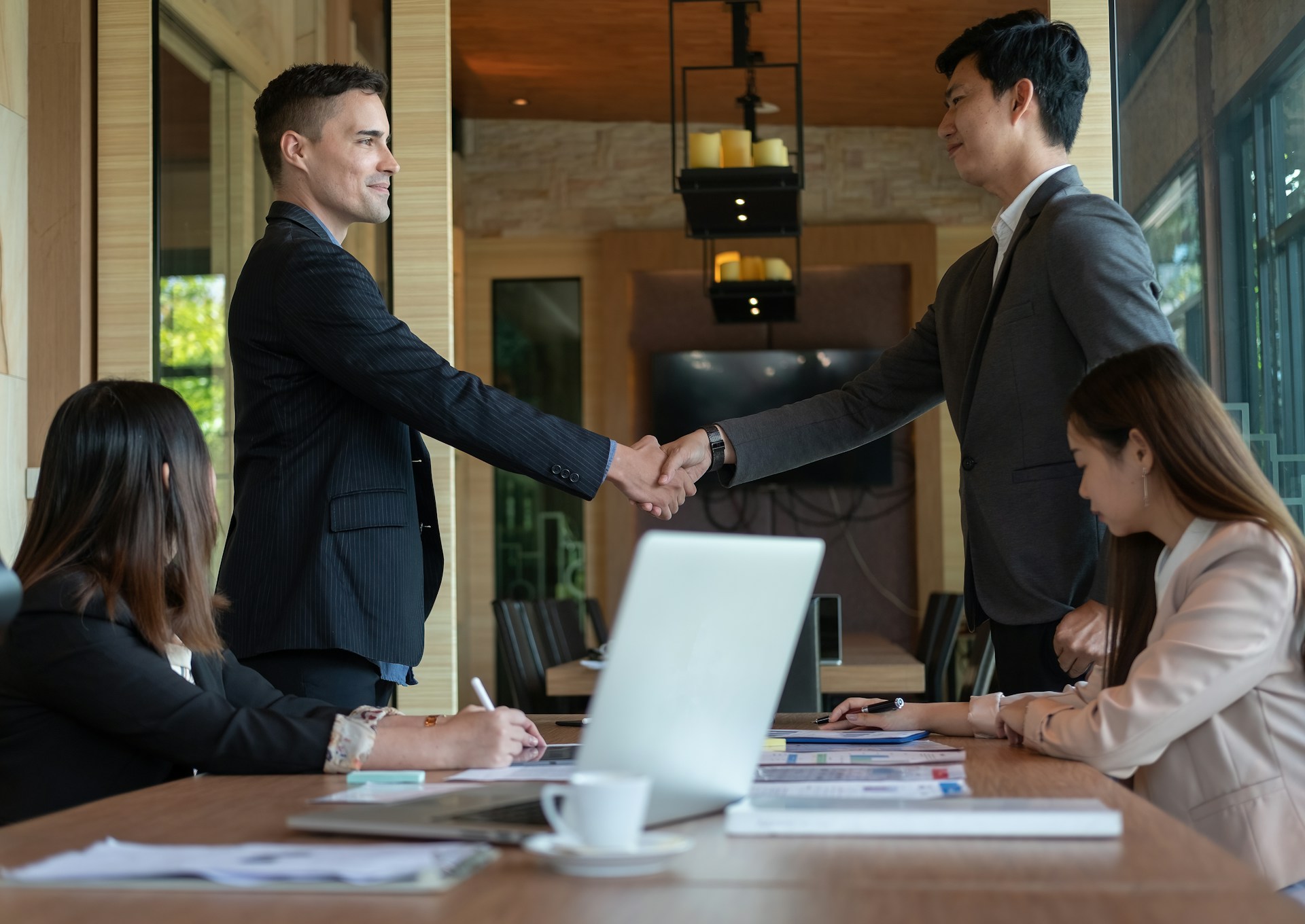
Navigating Microsoft’s 2025 pricing changes

Microsoft has announced new pricing changes that came into effect on the 1st April 2025. While the adjustments aren’t seismic, resellers have been dealing with the impact of these changes.
Proofpoint’s acquisition of Hornetsecurity

Explore the impact of the Proofpoint acquisition of Hornetsecurity on SMBs and MSPs across Europe. Learn why now is the ideal time to review your organisation’s security posture.
Why cybersecurity is no longer just the IT team’s job

Cybersecurity isn’t just IT’s job. Every department plays a role in protecting your organisation from modern threats.
Outlook’s new email rules: What high-volume senders must do by May 2025 | Topsec

From May 2025, Outlook will enforce strict SPF, DKIM and DMARC requirements for senders of 5,000+ emails/day. Learn what this means and how Topsec can help protect your email reputation.
The dangers of a data breach: Lessons from the 23andMe collapse

Discover the real impact of a data breach through the collapse of 23andMe. Learn how to protect your business with expert email security tips from Topsec.
Ensuring Business Continuity Amidst Microsoft 365 Outages | Email Continuity Solutions

Discover how email continuity solutions can keep your business running during Microsoft 365 outages. Learn how to prevent disruptions, maintain communication and protect data with Topsec Cloud Solutions.
Important Changes to NCSC’s Mail Check Program

Starting March 24, 2025, the NCSC will discontinue DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) Aggregate Reporting, DMARC Insights, and related TLS Reporting.
Post-poisoning: The silent cyber threats lurking in your inbox

Learn more about what post-poisoning is and how cybercriminals are using this new tactic to stay relevant and cause havoc.
5 Key Factors for Seamless Email Security Integration in Business
In today’s digital landscape, email security isn’t just an IT concern—it’s a critical part of your overall business strategy. Cyber threats are evolving, and a weak email security framework can put your entire organization at risk. From compliance requirements to employee awareness, integrating email security effectively ensures business continuity and data protection. In this blog, we’ll explore five key factors to help you align your email security measures with your broader business goals—keeping your company safe without disrupting productivity.

