Important Changes to NCSC’s Mail Check Program

Starting March 24, 2025, the NCSC will discontinue DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) Aggregate Reporting, DMARC Insights, and related TLS Reporting.
Post-poisoning: The silent cyber threats lurking in your inbox

Learn more about what post-poisoning is and how cybercriminals are using this new tactic to stay relevant and cause havoc.
Phishing Attacks in Different Industries: A Comprehensive Overview

Phishing attacks have become a widespread cybersecurity threat, affecting organisations across all industries. These attacks involve tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information, often through deceptive emails or websites.
The Evolution of Phishing Awareness Training

Phishing awareness training has evolved as hacking and phishing have grown in complexity.
Vishing (Voice Phishing): The Growing Threat and How to Protect Yourself

Learn about vishing, a type of voice phishing scam where fraudsters use phone calls to steal personal information. Discover how to protect yourself from vishing scams and stay informed with the latest cybersecurity tips to prevent fraud.
The Anatomy of a Phishing Email: How to Spot Red Flags and Stay Safe

To protect your organisation from ransomware and phishing attacks, it is important to know the anatomy of a phishing email. Read our blog to know more!
Safeguarding Against Quishing: Strategies for Enhanced Cybersecurity
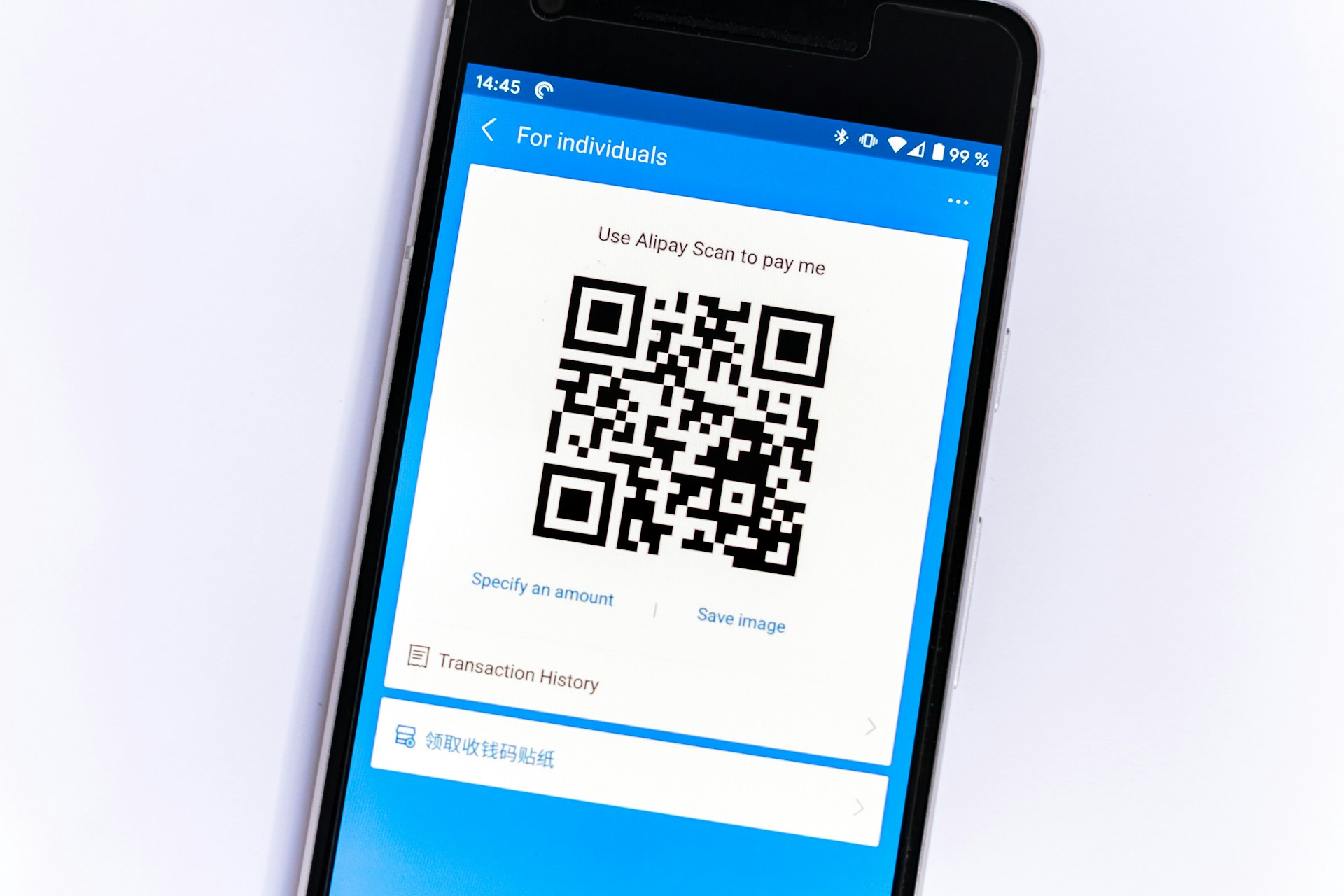
Explore effective strategies to secure your business from QR code phishing attacks, strengthen email security and implement robust cybersecurity measures.
Strengthening Microsoft 365 Security with Topsec Inbox Protect
Strengthening O365 with Topsec Inbox Protect We know having just one layer of O365 protection is not enough to secure your organisation. Get a Quote Download Datasheet Email Security > Strengthening Microsoft 365 Security with Topsec Inbox Protect With over 250 million monthly users, Microsoft 365 is a cornerstone of enterprise productivity. However, its popularity also makes it a prime target for cybercriminals. This article discusses the critical need for enhanced security in Microsoft 365 and introduces Topsec Inbox Protect as a formidable solution to these vulnerabilities. By Cian Fitzpatrick | 15th December 2023 Microsoft 365 Security Concerns The vast user base of Microsoft 365 encompasses a significant amount of sensitive data, which attracts malicious actors. Common security concerns include: Privilege Escalation Attackers gaining unauthorised system access. To mitigate this, implement role-based security controls, regular updates, multi-factor authentication, and privileged access monitoring. Bypassing Multi-factor Authentication Attackers may circumvent MFA, making it essential to use advanced MFA techniques, limit authentication attempts, and educate employees on phishing risks. Phishing Attacks Up to 20% of phishing emails evade detection by Microsoft 365’s defences, necessitating employee education, spam filters, and phishing simulations. Malicious Macro Disabling macros by default and using anti-malware software can prevent the execution of malicious code. Data Exfiltration To combat this, use DLP solutions, encryption, firewalls and educate employees on data security. Stay a step ahead of malicious actors Get Quote Topsec Inbox Protect: Fortifying Internal Emails Topsec Inbox Protect emerges as a vital layer of defence, specifically enhancing the security of internal emails in Microsoft 365 environments. How Topsec Inbox Protect Enhances Microsoft 365: Advanced Internal Mail Scanning Upon receipt of new internal mail, Inbox Protect performs rigorous security checks, quarantining any suspicious content. Comprehensive Threat Protection It addresses phishing, malware, ransomware, business email compromise, spam and unauthorised access. Dual-Defense Strategy When combined with Microsoft 365, it creates a two-pronged defence system, significantly enhancing overall email security. Ease of Use With a simple setup process, Inbox Protect starts securing historical emails within 14 days of integration. Key Benefits Enhanced Email Security Provides additional protection against a wide range of digital threats. Reduced Risk Lowers the chances of data breaches and unauthorised access. Improved Compliance Aligns with regulatory requirements, enhancing the organisation’s compliance posture. Learn how you can protect your staff Contact Us Conclusion In today’s digital landscape, relying solely on Microsoft 365’s inherent security features is insufficient. Topsec Inbox Protect offers an essential additional layer of security, particularly for internal email communication. By integrating this solution, organisations can significantly bolster their defences against a variety of cyber threats, ensuring a more secure and resilient digital environment. Secure your Microsoft 365 environment with Topsec Inbox Protect. Get a Quote for your Topsec Inbox Protect Free Trial and enhance your email security today!
Navigating the Quishing Threat: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
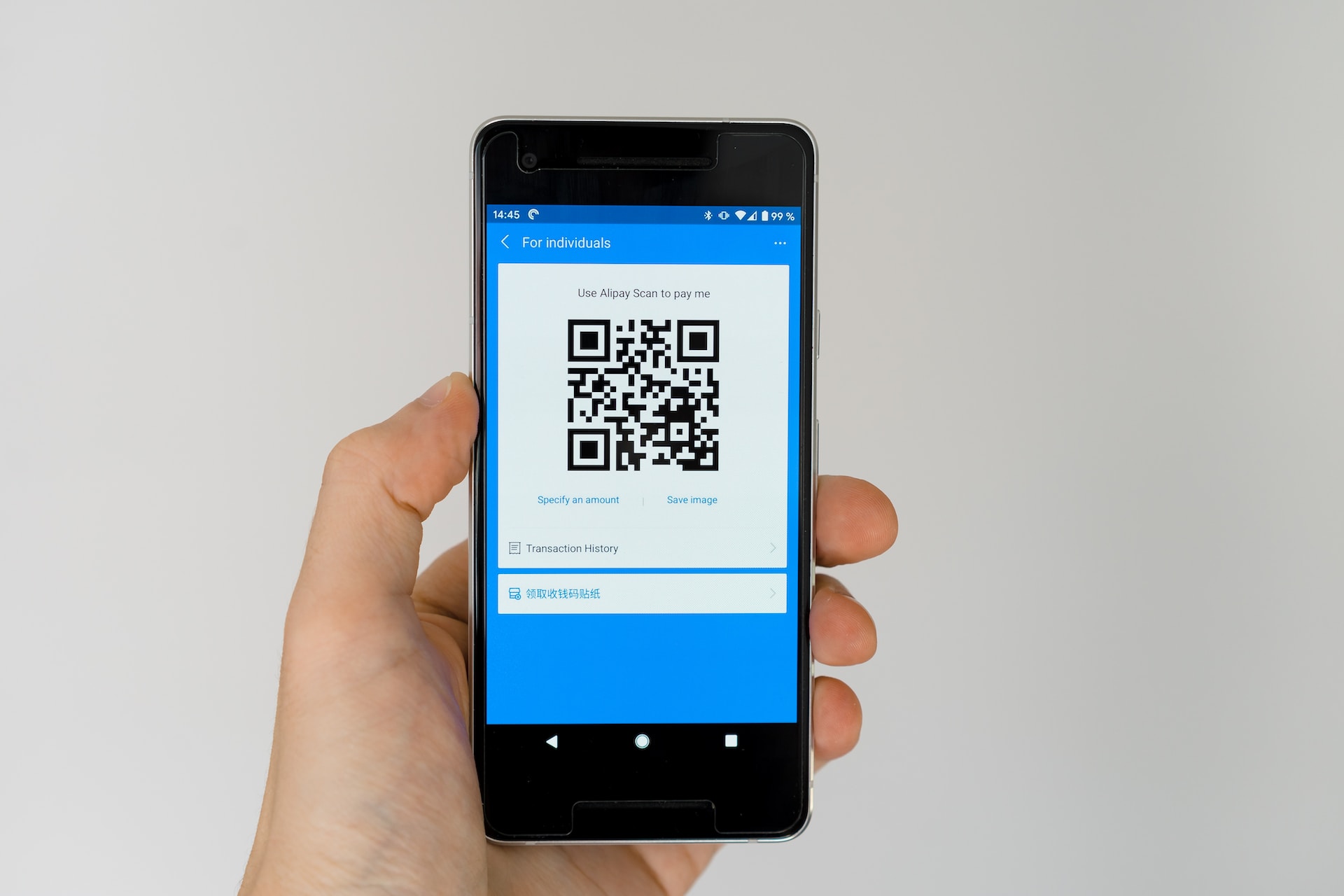
Unmasking Quishing: Decoding QR Code Phishing Quishing attacks are on the rise in business emails, know what to spot and how Get a Quote Download Datasheet Email Security > Phishing Unmasking Quishing: Decoding QR Code Phishing in the Modern Business World The integration of digital technologies into business operations has opened new avenues for convenience and efficiency. Quick Response (QR) codes stand out as a remarkable innovation in this regard. These square boxes filled with unfathomable squiggles simplifies access to information like never before. However, their rising popularity also brings to the forefront a new type of cyber threat: quishing, or QR code phishing. And the number one entry way for a quicking attack to bombard your organisation? Through your emails. (91% of all cyber attacks are through email.) By Cian Fitzpatrick | 6th December 2023 Deciphering Quishing: An In-Depth Look What Exactly is Quishing? Quishing is a cyberattack where QR codes are weaponised to execute phishing scams. This technique combines the ubiquity of QR codes with deceptive tactics to trick users into revealing sensitive personal and financial information. The Operational Dynamics of Quishing Quishing scams typically involve the creation and dissemination of fraudulent QR codes. These codes are strategically placed to replace or overlay genuine QR codes in public or business settings. When unsuspecting individuals scan these codes, they are redirected to counterfeit websites. These sites, designed to mimic legitimate ones, are traps for unwary users to enter their confidential data. Quishing in the Real World: Examining Case Studies Case Study: Quishing in Retail and Public Spaces One notable instance of quishing occurred in a retail environment where scammers replaced the QR codes on payment terminals with their counterfeit versions. Customers, intending to make payments, were instead led to fake payment portals, resulting in the theft of their credit card details. Case Study: Quishing in Corporate Environments In another case, a corporate office witnessed a quishing attack through seemingly harmless QR codes placed in its cafeteria. These codes, purportedly for accessing the daily menu, redirected employees to a phishing site that asked for their corporate login credentials. The Technical Mechanism: How Hackers Exploit QR Codes Hackers use QR codes as a medium to direct victims to phishing sites, cleverly camouflaging their malicious intent. These codes are strategically placed in locations with high foot traffic or within organisations, making them appear as legitimate parts of the infrastructure. The Hidden Perils of Quishing The subtlety of quishing lies in its ability to blend in with the everyday use of QR codes, making detection challenging. The delay in recognizing a quishing attack exacerbates its impact, as the stolen data can be exploited long before the breach is identified. Stay a step ahead of malicious actors Get Quote Fortifying Defences: Business Strategies Against Quishing Comprehensive Strategies for Business Protection 1.Enhanced Employee Awareness Regular workshops and training sessions to educate employees about the nuances of quishing. 2.Advanced QR Code Security Employing QR codes with enhanced security features like encryption and tracking to prevent unauthorised alterations. 3.In-depth Cybersecurity Protocols Implementing advanced cybersecurity solutions, including next-generation anti-malware and anti-phishing systems. 4.Proactive Monitoring and Response Establishing a robust monitoring mechanism to detect and respond to any signs of quishing promptly. 5.Selective and Mindful QR Code Utilisation Encouraging a culture of cautious QR code usage, where employees verify the source before scanning. Building a Quishing-Resilient Business Environment In the digital age, staying ahead of cyber threats like quishing is imperative for business security. By understanding the mechanics of quishing, staying alert to its manifestations, employing robust cybersecurity measures, and fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance, businesses can effectively shield themselves from these sophisticated attacks. The fight against quishing is not just about technological solutions. It’s equally about cultivating an informed and cautious digital environment. Contact Topsec today to fortify your organisation’s email security. Our client case studies illustrate the care and commitment we bring to our work. Our team will do this for your organisation too. Learn how you can protect your staff Contact Us
What is Spear Phishing?

What is Spear Phishing? It is considered to be the most potent form of attack, learn how you can prevent these attacks. Get a Quote Download Datasheet Email Security >Phishing What is Spear Phishing? Among different cyberattacks, spear phishing poses the most potent threat. Unlike standard “Spray and Pray” phishing, spear phishing is a highly targeted and deceptive form of attack. It integrates sophisticated social engineering techniques, often going unnoticed by its target. In addition, according to Symantec’s Internet Security Threat Report(ISTR), 65% of attackers relied on spear phishing attacks. So, it’s highly important to understand what spear phishing is to create a protective shield against it. By Cian Fitzpatrick | 16th November, 2023 Spear Phishing Definition Spear phishing is a type of phishing attack that targets highly specific individuals or roles within an organisation to acquire sensitive information. Spear phishing is much more effective than a standard phishing attack. The attacker does intensive research on their target and uses social engineering techniques to craft a message to make it seem to be from a legitimate source. For instance, they collect personal information about a target and send messages disguising themself as a trustworthy friend to acquire sensitive information. Types of Spear Phishing Attacks Some of the major spear phishing types are: 1. Whaling Phishing It is a highly targeted attack that targets high-profile or high-ranking individuals such as C-suite executives or board members. It also involves non-corporate targets such as celebrities or politicians. Attackers aim to fetch large sums of cash or acquire confidential information that can be used against them—no wonder it requires more research than any other form of spear phishing attacks. 2. Business Email Compromise(BEC) CEO Fraud The threat actors impersonate or hack into the email account of a senior executive, typically a CEO. And instruct lower-level employees to wire money into fraudulent accounts by creating a sense of urgency to make them act abruptly. Email Account Compromise(EAC) Attackers gain access to lower-level employees to send fraudulent emails and trick other employees into sharing confidential information. EAC is often used to acquire the credentials of senior executives to perform CEO fraud. Barrel Phishing It is a phishing attack where scammers send emails to a large number of recipients, pretending to be from a legitimate source. The scammers anticipate that at least one recipient will click on the link to steal sensitive information. Try Our Phishing Simulator Now Get Quote How Does Spear Phishing Attack Work? Spear phishing attack works in various stages; they are: Selection of Target Scammers choose individuals or organisations they want to target based on their goals, whether their goal is to gain large sums of money or sensitive information. Use of Reconnaissance Technique Before commencing the attack, the scammer gathers detailed information about the victim using social media platforms. Crafting Email By using gathered information, scammers craft a personalised email to make it look as if it’s from a legitimate source. This causes the target to immediately lower their guard. For instance, it could be a coworker, manager, or a trustworthy friend of the target. Call to Action Fraudulent emails often have a call to action to create a sense of urgency to ensure the attack works 100% of the time. In the heat of the moment, the target will click the link or download an attachment. This action can lead to serious consequences, including identity theft, data breaches, ransomware attacks, corporate espionage, etc. Covering Footprints After the attack, the scammer removes every trace of the attack to evade detection and prolongs access to the system. Common Targets of Spear Phishing Attacks Spear phishing attacks involve detailed research of a high-value or high-profile individual. Even though they are often time-consuming, they yield a higher anticipated reward than standard phishing attacks. Commonly targeted individuals of spear phishing attacks are: High profile individual Scammers target high-profile individuals like CEOs, politicians or celebrities to steal their sensitive information. Lower-level or New Employees Lower-level or newer employees often fall victim to phishing attacks, as they are frequently unaware of policies or procedures they must follow to prevent spear phishing attempts. Specific Group or Types of Employees Scammers target employees with access to sensitive or confidential information, such as HR or finance executives. Learn how you can protect your staff Contact Us Spear Phishing Characteristics Some of the characteristics of spear phishing are: Targeted Recipients Spear phishing employs highly personalised messages to target specific individuals or organisations. These messages focus on high-profile or high-value individuals, promising substantial rewards. Spear phishing targets specific individuals, unlike standard phishing, which targets a high volume of individuals. Personalised Messages Scammers on various social media platforms conduct intensive research on their targets to formulate emails that create a sense of familiarity, often leading to the disclosure of sensitive information. Sophisticated Tactics and Techniques Scammers use reconnaissance and social engineering techniques to carry out spear phishing attacks. The reconnaissance technique involves intensive gathering of information on a target. At the same time, social engineering techniques involve the manipulation of personality traits to make the target perform a certain action. Common Objectives Spear phishing takes on various forms, but the goal remains the same: extracting sensitive information such as credentials or credit card information. Links to Malicious Websites or Files Scammers use phishing emails, which include links to malicious websites or files created by threat actors, to extract sensitive information when recipients click on them. Common Techniques Used in Spear Phishing Attacks Some of the characteristics of spear phishing are: Social Engineering Techniques Spear phishing attacks thrive on social engineering techniques. They manipulate personality traits such as desire to be helpful or curiosity about events or news. Individuals let their guard down easily with this technique, enabling threat actors to leverage the situation to extract sensitive information. Suspicious Emails and Phone Calls Attackers, using generic or misspelt domains in their emails, disguise themselves as legitimate entities to reach out to their targets through emails and phone calls. Malicious Emails with Attachments or Links

