Home » How Does DMARC Work?
Email communication is a crucial aspect of daily operations when you run an organisation. You and your team exchange emails daily, which may contain sensitive information that could be compromised by various risks. Therefore, the security of your email communication becomes crucial.
By Cian Fitzpatrick | 3 August, 2023

Taking the necessary measures to safeguard your email communication will help protect your organisation’s valuable data and maintain your stakeholders’ trust. Hence, DMARC services (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) play a powerful solution to enhance your organisation’s email security.
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance, a security protocol used to authenticate an email. It protects domain owners from spam, phishing, and other email scams that can happen through email.
It combines two essential components such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail), that provide a framework to verify the authenticity of incoming email messages. Take a look at our comprehensive DMARC guide to get all the necessary information.
Through SPF (Sender Policy Framework), you can specify which IP addresses can send emails from your domain. When an email is received, the receiving email server checks the SPF record to verify if the sender’s IP address is authorised to send emails for that particular domain. If the email fails the SPF check, it is considered potentially fraudulent.
“DNS (Domain Name System) acts as a phonebook for the internet. When you type a domain name like “example.com” into your web browser, the DNS system translates that domain name into the corresponding IP address (such as 192.0.2.1) that identifies the server where the website is hosted. “
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is an email authentication method that adds an extra layer of security by digitally signing outgoing emails with a private key and attaching the signature to the email headers. The recipient’s server then uses the public key published in the DNS to verify the authenticity and integrity of the email. This ensures that the message originated from the authorised domain.
However, SPF and DKIM alone cannot fully protect against email fraud. This is where DMARC plays an important role. It builds upon SPF and DKIM to provide a comprehensive framework for email authentication and policy enforcement.
DMARC, SPF, and DKIM work together to authenticate emails and prevent fraudulent activities.
Together, these protocols prevent email fraud, phishing, and spoofing attacks, providing more secure email communication.
DMARC is a flexible protocol that domain owners can customise based on their needs. The technical specifications of DMARC are as follows:
A DMARC record is a simple text file that stores a domain’s DMARC policy. It instructs email receivers on what actions to take when an email fails DMARC authentication and where to send reports.
The DMARC record includes various parameters, such as the chosen DMARC policy, which determines how emails that fail DMARC validation are handled.
DMARC allows domain owners to specify different policy modes if an email fails the SPF or DKIM process. There are three different policy modes, such as “None,” “Quarantine,” and “Reject.”
Two alignment checks known as SPF Alignment and DKIM Alignment ensure the “From” header domains match the authenticated domains used in SPF and DKIM.
DMARC sends reports to domain owners known as “Aggregate Reports” and “Failure Reports”. These reports provide SPM and DKIM statistics, alignment results, sending sources, and more.
DMARC allows domain owners to specify separate policies for subdomains to enable control over email authentication for different subdomains.
DMARC uses a specific syntax to provide instructions or information. The common tags used in DMARC records include “v” for protocol version, “p” for policy, “rua” for aggregate report addresses, “ruf” for failure report addresses, and “sp” for subdomain policies.
DMARC offers domain owners and organisations a framework to specify how email receivers should handle unauthenticated emails that claim to come from their domain. It helps to ensure the safety and security of email communication.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how DMARC works:
This process enhances security, improves email deliverability, and maintains compliance with DMARC policy.

It is essential to regularly check the DMARC configuration, review reports, and make any necessary adjustments for better efficiency and proper implementation.
Tools such as SPF validators and DKIM checkers help validate the records and ensure they are correctly set up.
Many malicious attackers attempt to deceive recipients into sharing sensitive information, such as financial details or login credentials, by impersonating them via email. DMARC plays a crucial role in combating these phishing attacks.

Selecting a DMARC service provider is a crucial process that requires domain owners to evaluate various factors carefully.
Below are some checklists to consider while choosing a DMARC service provider:
Topsec Cloud Solutions offers comprehensive DMARC services to address businesses’ email security concerns. As the only managed email service provider, we provide an end-to-end service, ensuring that all your email security needs are met efficiently. Our DMARC services leverage AI and machine learning models for ultimate threat protection, analysing millions of emails daily.
Partner with Topsec for reliable and effective DMARC services, enhancing your email security framework with our expertise and AI-driven approach. Our technical professionals are available 24/7, providing round-the-clock support. Let us manage your entire DMARC process, so you can focus on your business needs.
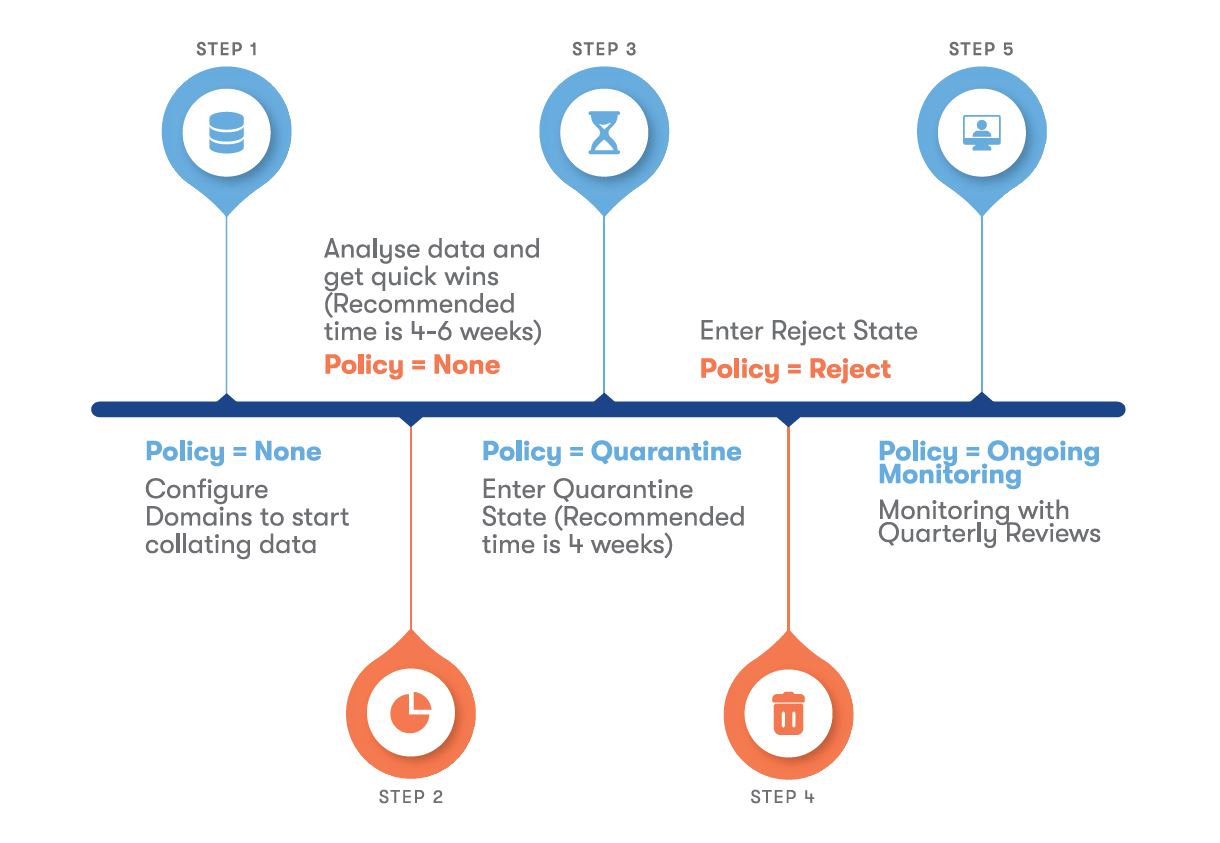
Many organisations are realising the importance of DMARC and are rapidly adopting it. The evolution of email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC will result in a stronger mechanism for verifying email authenticity, which makes email communication more secure.
DMARC will play a central role in comprehensive email security frameworks, integrating with advanced threat detection technologies, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. This layered approach will enhance overall email security and safeguard against emerging threats.
The future of DMARC and email security is dynamic. With increased technological advancements, collaboration, and user education, DMARC will continue to be a critical component of email security strategies, ensuring secure and trustworthy communications channels for domain owners and organisations.
Yes, DMARC relies on SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) to ensure the authenticity of the sender’s domain. SPF verifies the sender’s IP address, and DKIM verifies the integrity of the email’s digital signature. SPF and DKIM work together to provide a layered approach to email authentication, and DMARC builds upon their foundations to enforce policies and provide reporting capabilities.
DMARC works by verifying the authenticity of emails through SPF and DKIM checks and aligning the “From” header domain with the authorised domains. It enforces policies for handling unauthenticated emails, such as marking them as spam, quarantining them, or outright rejecting them. DMARC also generates aggregate reports that provide insights into email authentication results, sources of abuse, and potential configuration issues.
Email receivers primarily implement DMARC to check the presence of a DMARC record in the sender’s domain DNS. However, it also allows senders to control how they handle unauthenticated emails.
Thus, it collaborates between senders and receivers to enhance email security and deliverability.
A domain should have only one DMARC record. Having multiple records for the same domain can lead to inconsistent policies, and email receivers won’t know which one to follow. This will lead to potential deliverability issues and misinterpretations of intended policies. If you need to modify your DMARC policy or configuration, updating the existing DMARC record is recommended rather than creating additional ones.
