Home » What is DMARC? A Complete Guide
DMARC is an open email authentication protocol that provides robust domain-level fortification of the email communication channel. It is a robust shield protecting email domain owners from unsolicited exploitation and malicious activities. DMARC is a protocol—essentially a set of rules—that dictates how email receivers and senders handle email authentication.
By Cian Fitzpatrick | 18 July, 2023

DMARC significantly diminishes the likelihood of phishing and spoofed emails breaching security and ending up in an end user’s inbox. It has proven an indispensable ally in the relentless battle against email-related cybersecurity threats.
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance. It functions as a roadmap to guide the email authentication process. It offers email domain owners a mechanism to defend against misuse and potential cyber threats while ensuring the unhindered flow of authorised emails.
DMARC in email operates as a steadfast security guard for your domain. It’s a policy allowing domain owners to specify that their emails are protected by SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). It communicates to the recipient’s mail server how to handle emails from your domain that fail SPF and DKIM checks—thereby adding an additional layer of authenticity and security.
DMARC is a vital line of defence in email security, following SPF and DKIM. When an email arrives, the recipient’s mail server initiates a DMARC check. This check involves verifying whether the email aligns with the DMARC policy specified by the domain owner. If the email passes the DMARC check, it lands safely in the recipient’s inbox. If it fails, however, the recipient’s mail server takes action according to the DMARC policy—either marking the email as spam, rejecting it entirely, or delivering it with a warning. If you’re curious about the intricate details of the verification process, delve deeper by reading our comprehensive post on How does DMARC work?
DMARC comprises several integral components, each performing a unique function in the email authentication process. There are three key components- DMARC Record, DMARC Report and DMARC Authentication. Understanding these components can greatly enhance your ability to leverage DMARC for improved email security.
A DMARC record is a text (TXT) entry in your domain’s DNS (Domain Name System) record. It specifies the DMARC policies for your domain. When a recipient’s mail server receives an email from your domain, it checks the DNS for your DMARC record to determine how to handle the email. DMARC record lets you decide whether to reject, quarantine, or accept emails that fail DMARC checks.
A DMARC report is a document generated by the recipient’s mail server after it has checked an email against your DMARC policy. It provides vital information on who is sending emails on your behalf, the number of emails sent, and the number of those emails that passed or failed DMARC checks. DMARC reports are invaluable for identifying potential issues and ensuring your email authentication protocols work as intended.
DMARC authentication is the process by which the recipient’s mail server verifies an email against the DMARC policy specified in your DNS. It checks whether the email passes SPF and DKIM checks and whether the domain in the DKIM signature or the domain in the email’s return-path (envelope from) aligns with the domain in the email’s header-from. The email is authenticated if it passes these checks; if not, the mail server takes action as specified in your DMARC policy.
Email authentication can often appear as a complex maze of acronyms. Appreciating how these different security measures—DMARC, SPF, and DKIM—interact and complement one another is important.
DMARC, SPF, and DKIM are all authentication methods designed to secure your emails against misuse and forgery. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) enables domain owners to specify which servers can send emails on their behalf. Meanwhile, DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) provides an encryption key and digital signature that verifies that an email message was not faked or altered.
DMARC unifies the SPF and DKIM authentication mechanisms into a common framework. It allows domain owners to declare how they would like an email from that domain handled if it fails authentication.
A DMARC policy is a specification that the domain owner sets in their DMARC record. It instructs the recipient’s mail server on actions to take if an email fails DMARC authentication. The policy can be set to none (take no action), quarantine (mark as spam or segregate), or reject (discard the email).
Choosing the right DMARC policy depends on your organisation’s risk appetite and your confidence in your email authentication setup. If you’re beginning with DMARC, a ‘none’ policy can be a good starting point for monitoring your email flow. Once you’ve optimised your SPF and DKIM setups and are confident about the legitimacy of your outgoing emails, you can move to a ‘quarantine’ policy and eventually a ‘reject’ policy for full protection.
To implement DMARC, you must ensure your emails are SPF and DKIM-compliant. Next, you publish a DMARC record in your DNS with a ‘none’ policy for monitoring. After analysing the DMARC reports and resolving any issues, you can gradually move to a ‘quarantine’ and then a ‘reject’ policy.
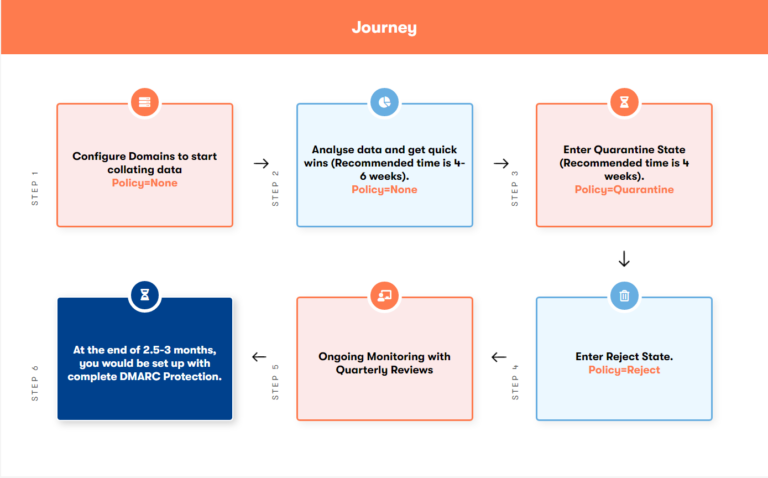
DMARC implementation can sometimes be complex, with challenges like ensuring SPF and DKIM compliance, understanding DMARC reports, and managing a large number of sending sources. A comprehensive DMARC solution like Topsec Cloud Solutions offers can help overcome these hurdles. Topsec DMARC protection provides easy setup, clear report analysis, and efficient handling of authorised sending sources.
DMARC brings several significant benefits to your organisation, from enhancing email security to improving sender reputation. Below are listed the top 5 benefits of DMARC.
Implementing DMARC is a proactive approach to secure your email domain from phishing attacks, spoofing, and other fraudulent activities. It provides an additional layer of security that verifies the sender’s authenticity and the integrity of the message content.
DMARC increases email receivers’ trust in your messages and improves your overall email deliverability rate. It reduces the likelihood of your emails ending up in the junk or spam folder.
Spoofing can seriously harm your brand reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust. DMARC prevents fraudulent use of your domain and helps protect your brand. It ensures your customers only receive legitimate communications from you.
DMARC policies allow you to decide how you want receivers to handle emails that fail authentication, helping to reduce the number of fraudulent emails that reach your customers’ inbox.
DMARC reporting provides comprehensive visibility into your email channels and helps you identify legitimate and fraudulent senders for your domain.

Data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, have made email security more critical than ever. Complying with DMARC and GDPR is crucial for organisations to maintain trust and safety in their digital communications while respecting and upholding individual privacy rights.
DMARC protects email data from unauthorised access and misuse, helping with GDPR compliance. They prevent email spoofing and significantly reduce the risk of data breaches that could lead to hefty GDPR fines. Moreover, DMARC reporting can also help demonstrate ongoing compliance efforts. It provides clear evidence of monitoring and addressing email security threats.
DMARC works with third-party email services. It requires them to be authenticated as authorised senders for your domain. This means they must pass SPF and DKIM checks from their servers. Topsec Cloud Solutions can assist you in setting up this process, ensuring all third-party email traffic is DMARC compliant.
DMARC ensure that only legitimate emails from your domain reach the recipient’s inbox, ultimately preventing phishing. Using DMARC’s ‘reject’ policy, you can effectively block all emails that fail DMARC checks, thereby stopping phishing emails impersonating your domain from reaching your clients or employees.

BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification) is an emerging email standard that works alongside DMARC. BIMI allows your company’s logo to appear in recipients’ inbox, but requires DMARC enforcement as a prerequisite.
BIMI is an email specification that allows brands to display a logo next to their emails in the recipient’s inbox, promoting trust and recognition. However, implementing BIMI requires a strong DMARC policy (preferably ‘reject’), thereby enhancing the brand’s email security while improving its visibility.
The versatility and inclusivity of DMARC make it a resource that is not limited to any specific industry or size of the organisation. From small businesses to large corporations, non-profits to government entities, educational institutions to independent contractors, DMARC can enhance email security.
Companies that use email for internal or external communication can greatly benefit from implementing DMARC. It is especially useful for organisations that deal with sensitive information, including banks and e-commerce platforms.
When it comes to leveraging DMARC for email security, there are several best practices that you should consider. Below are a few DMARC best practices to keep your organisation’s email communications safe.
Implementing DMARC is a proactive approach to secure your email domain from phishing attacks, spoofing, and other fraudulent activities. It provides an additional layer of security that verifies the sender’s authenticity and the integrity of the message content.
Just having a DMARC record isn’t enough. Regularly monitor your DMARC reports to spot anomalies, adjust policies, and maintain email security.
DMARC is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution. It’s a living, breathing entity that needs to be nurtured and adjusted per your organisation’s needs. As your email traffic patterns change, so should your DMARC policies.

As we venture into the digital future, the role of DMARC in email security is set to become even more significant. With email threats on the rise, there is a pressing need for robust protective measures.
Industries across the globe have recognised the potential of DMARC, leading to a steady increase in its adoption. Internet service providers, email service providers, and companies of all sizes embrace DMARC to protect their brand, increase email deliverability, and ensure that phishing scams don’t reach their customers’ inboxes. Governments are also increasingly mandating the use of DMARC for public sector organisations.
DMARC reports are incredibly valuable for understanding a company’s email ecosystem and identifying potential vulnerabilities. The future will likely see more advanced reporting features with actionable insights and real-time threat detection. The rise of AI and machine learning could also play a significant role here, providing the ability to analyse large volumes of data and detect anomalies faster.
Integration with other email security technologies, like Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI), is an upcoming trend. BIMI allows companies to display their logo in their customers’ inboxes, increasing brand visibility and trust. By integrating DMARC with BIMI, companies can significantly enhance their email authentication strategy.
As cyber threats evolve in sophistication, DMARC in the digital landscape becomes increasingly critical. Below is explained how DMARC is adapting to stay ahead of these challenges.
Expect continuous improvements in the DMARC technology, incorporating advanced features to mitigate modern cyber threats. This could include predictive algorithms, anomaly detection, and machine learning-enabled threat analysis.
The widespread adoption of DMARC doesn’t solely rely on its technical superiority. Understanding DMARC’s benefits and implementation process is equally important. Therefore, user education will be more focused – through webinars, online courses, and detailed guides. This push for awareness will empower organisations to take full control of their email security.
DMARC, on its own, is a powerful tool, but its effectiveness increases when used in conjunction with other email security measures. In the future, we can expect more collaborations and partnerships between DMARC and other cybersecurity firms to offer users a more comprehensive security suite.
Strict DMARC policy enforcement may become the norm rather than the exception. Currently, many organisations use DMARC in ‘monitor mode,’ but as email threats continue to rise, more organisations may shift to a ‘reject’ policy, providing stronger protection against phishing and spoofing attacks.
DMARC is a powerful email authentication protocol that can dramatically improve your email security and deliverability while protecting your brand and boosting customer trust. Implementing DMARC may seem like a complex task, but with the right tools and guidance from experts can become a manageable and highly beneficial process.
Topsec Cloud Solutions can help you in your journey towards enhanced email security with DMARC. As a leading email security solution provider, we are well-equipped with the knowledge, tools, and resources to guide you through the DMARC implementation process. From creating and monitoring DMARC records to troubleshooting issues, our expertise lies in offering customised solutions to meet your specific needs. Connect with us and empower your email communication security with our DMARC security solution.
DMARC is specifically designed to authenticate email messages and protect against email spoofing and phishing.
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that uses SPF and DKIM to verify the authenticity of an email message.
Technically, yes. However, it’s not recommended because SPF and DKIM together provide a robust level of email security, and most DMARC policies require both to function effectively.
Yes, but similar to SPF, it’s not recommended. SPF and DKIM provide unique security features that enhance the overall effectiveness of DMARC.
DMARC significantly enhances email security by verifying the authenticity of email messages, thereby protecting against email spoofing and phishing attacks.
Gmail uses DMARC to authenticate incoming emails and determine their delivery to users’ inboxes.
Read our latest blog post to Unpack the Latest DMARC Email Authentication Requirements set by Gmail and Yahoo. Essential reading for high-volume email senders exceeding 5,000 daily emails. Understand the new protocols to ensure your emails remain trusted and visible.
